
Flame retardant polyamide (cotton) fiber-fabric can also be safer
With the development of national economy and the progress of industrial production level, more and more textile varieties have entered people's daily life, and the problem of disaster caused by textile ignition has become more and more serious. The results of the fire investigation show that fires caused by the ignition and spread of textiles that do not have flame retardant properties account for more than 20% of all fire accidents, such as the fire in Karamay Friendship Hotel in Xinjiang and the fire in Yiyuan Song and Dance Hall in Fuxin, Liaoning, which are caused by the burning and spread of curtains and sofas respectively.

Figure 1 Application of textile products
The Flame Retardant Association (EFRA) has conducted a survey and found that 5000 people in Europe alone lose their lives due to fires every year, which is equivalent to 1 to 2 people in 100000 people. According to the annual fire statistics in the UK, 20% of the fires in the UK are caused by the burning of textiles, but the death rate caused by these 20% fires accounts for more than 50% of all deaths. The frequent occurrence of fire accidents has also brought serious losses of life and property to our country, as shown in Table 1.
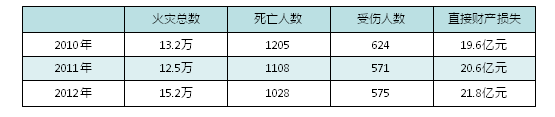
Table 1. Fire statistics in China in recent years
Polyamide (Polyamide) is the first synthetic fiber to achieve industrial production, and its output accounts for the second place of all synthetic fibers. The main varieties include cotton 6, cotton 66 and so on. Although cotton fiber does not belong to flammable fiber, but because of its melting temperature and ignition point temperature difference is large, in the combustion prone to shrinkage and melting dripping phenomenon, and then spread the fire, ignition of other substances, so in the practical application of the potential fire risk is greater, (Figure 2). With the improvement of people's awareness of safety and environmental protection, how to improve the flame retardancy of fabrics and reduce potential risks has become the focus of increasing attention.
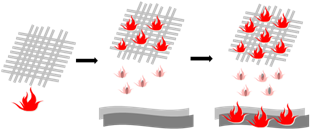
Fig. 2 Fire Expansion Caused by Melting Drop of Polyamide
At present, the improvement of the flame retardancy of cotton fiber can be considered from two aspects:
I. Improvement of Flame Retardancy of Polyamide Fiber Itself
This kind of way mainly through copolymerization or blending, improve the flame retardant performance of the fiber itself, with permanent flame retardant, environmental protection advantages, but the cost is relatively high.
① Copolymer flame retardant modification, in the process of the synthesis of cotton with flame retardant properties of the comonomer, the use of flame retardant monomer and cotton monomer reaction activity between the synthetic polymer matrix itself has flame retardant properties. The main comonomers used in cotton are phosphorus, sulfur, halogen, etc.
The flame retardant blending modification, that is, the flame retardant is added to the cotton polymer and spun directly, and the selected flame retardant must meet the following conditions: the thermal stability of the flame retardant is better than the cotton fiber; the melting temperature is slightly lower than the spinning temperature; the decomposition temperature is much higher than the spinning temperature; the flame retardant has good compatibility with the cotton fiber.
There are many flame retardants that can be used in cotton: low molecular weight phosphorus-containing compounds in phosphorus-based flame retardants; brominated pentaerythritol and chlorinated polyethylene in halogen-containing flame retardants.
II. Flame Retardant Finishing of Fabric
Flame retardant finishing is by grafting, baking, coating and spraying on the surface of the cotton fabric molding covered with a layer of flame retardant, so as to improve the flame retardant products. Compared with the copolymerization/blending method, this method is simple in process and convenient to operate, but it may reduce the strength and washability of the fabric, and affect its appearance and feel.
① Reactive type, the surface of the cotton fiber has a certain activity due to the amide group, which can be replaced with some reactive flame retardants to obtain flame retardancy. For example, at 200 degrees C, the cotton fiber is immersed in the halogen-containing reactive flame retardant solution for treatment, and the fabric fiber with flame retardancy can be obtained.
② Non-reactive type, which attaches the flame retardant to the fiber surface through adsorption deposition, non-polar van der Waals force bonding, adhesive bonding and other forms to play a flame retardant effect. Because the method uses a physical combination, the flame retardant component is difficult to penetrate into the interior of the fiber, so that the flame retardant effect of the fabric can not be maintained for a long time, while affecting the fabric wash resistance.
With the expansion of the application field of cotton fiber and the progress of science and technology, the research of flame-retardant cotton fiber fabric will also make more breakthroughs, and the future trend will mainly focus on the development of halogen-free environmental protection cotton fiber, non-melt-drop flame-retardant cotton fiber, and functional flame-retardant cotton fiber.







