
Application of Super Tough Flame Retardant PBT Engineering Plastics in the Field of Electronic Connectors
1. what is a connector
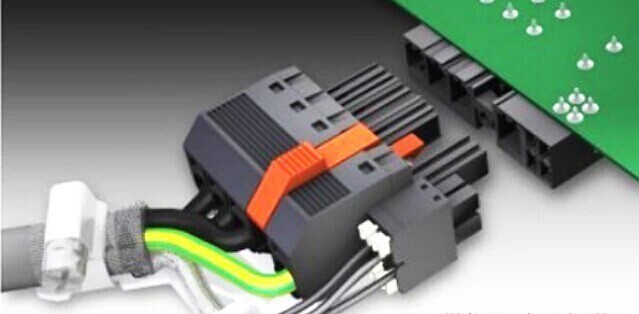
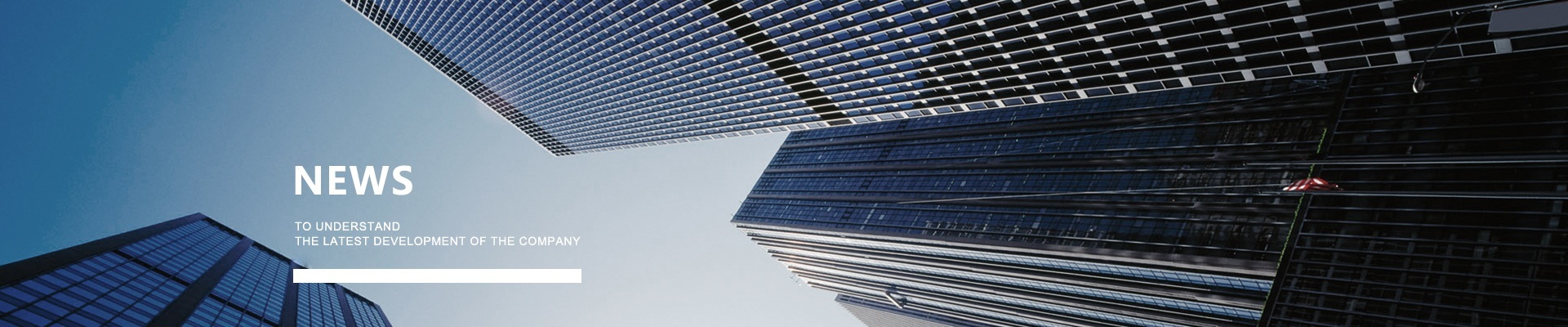
Connectors are also called connectors (connector), also known as connectors and sockets, generally refers to electrical connectors. That is, a device that connects two active devices and transmits current or signals. The main features of the connector include the following aspects:
1) Improve the production process: simplify the assembly process and mass production process of electronic products;
2) Easy to repair: If an electronic component fails, the connector can quickly replace the failed component;
3) Easy to upgrade: with the progress of technology, the connector can quickly update parts;
4) Improve design flexibility: Connectors allow engineers to have greater flexibility when designing and integrating new products and when using components to form systems.
Therefore, where there is a signal or current transmission or transit, the basic connector will be used. Connectors are widely used in electronic communication equipment, automobiles, home appliances and other fields, such as various earphone speaker sockets, printed circuit board connectors in electronic equipment, various cable connectors, and integrated circuit connectors of various specifications.
Features of engineering plastics for 2. connectors
Because the connector is basically used in the field of electrical and electronic, this field has higher requirements for the mechanical properties, electrical properties, temperature resistance and flame retardancy of engineering plastics. The engineering plastic materials for connectors must have the following characteristics:
1) Stable contact resistance
2) Good durability, long-term use
3) Small size and light weight
4) Good engagement and separation
5) Good electrical insulation performance
6) Easy installation and maintenance
Application and Characteristics of 3. Super Tough Flame Retardant PBT in Connector Field
1) Excellent toughness:
Toughness (toughness) characterizes a material's ability to absorb energy during plastic deformation and fracture. The better the toughness, the less likely the material is to undergo brittle fracture. Generally, the impact strength is used to measure the toughness of the material. The notched impact strength of modified PBT engineering plastics for universal connectors is about 10-15KJ/m2, and the notched impact strength of this super-tough flame retardant PBT reaches 55KJ/m2.
The impact strength of super-tough PBT is compared with that of ordinary PBT engineering plastics (Figure 1 and Figure 2):
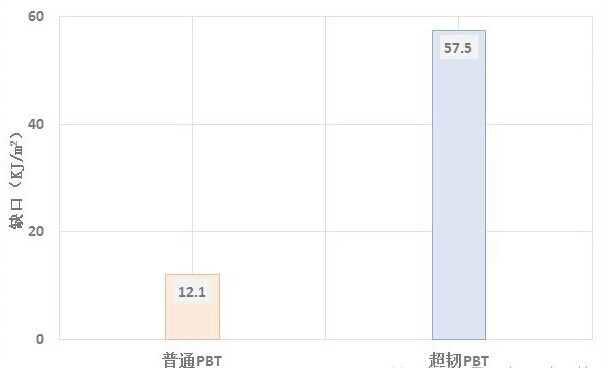
Fig. 1 Comparison of notched impact strength
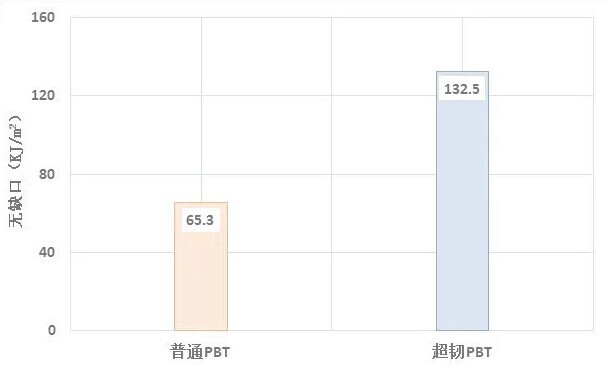
Fig. 2 Comparison of unnotched impact strength
The following figure is an electron scanning microscope (SEM) photo of the impact section of the super-tough modified PBT engineering plastic and the ordinary modified PBT engineering plastic. It can be clearly found in the figure that the ordinary modified PBT section is smooth, showing typical brittle fracture (brittle fracture) characteristics, brittle fracture spline without obvious deformation and fracture, fracture material almost no plastic deformation.
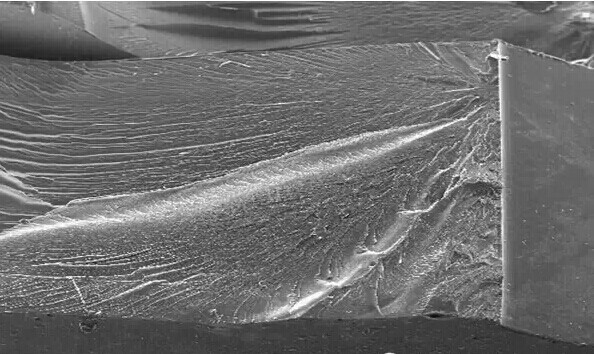
Fig.3 SEM image of spline section of ordinary modified PBT material
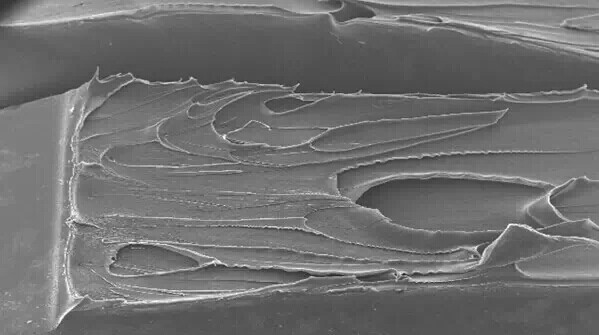
Fig.4 SEM image of spline section of super-tough modified PBT material
However, the ultra-tough PBT engineering plastic presents the opposite fracture surface morphology, and the cross-section surface has obvious strip-like ribbon morphology. This "strip-like ribbon" morphology indicates that before the fracture of the material, significant plastic deformation occurs and ductile fracture (ductile fracture) occurs under the condition that the deformation cannot support the impact of external force. Under the condition of the same external force, the greater the plastic deformation occurs during the impact, the ability to absorb and dissipate external energy is also stronger.
Looking at the above data and microscope photos, some readers may wonder what is the relationship between these so-called data and the actual application of electronic connectors?
We might as well do a simulation experiment: 90 ℃ angle repeated folding experiment
Ordinary PBT engineering plastics and Blue Star Super Tough PBT are made into 1mm thick parts (as shown in the figure), and the thickness of the folded part is 0.5mm. Return the part to the original place after folding at 90 ℃, repeat it for many times, and observe the phenomenon.

Ordinary modified PBT engineering plastics, broken after repeated folding 20 times

Super Tough PBT Folding 50 Times Super Tough PBT Folding 100 Times Super Tough PBT Folding 200 Times
The super-tough PBT is folded 50 times, 100 times and 200 times at 90 ℃: no fracture and no peeling.
This excellent bending resistance can ensure that the electronic connector material is not easy to break during the plugging and unplugging process, and the super-tough PBT material has higher quality and service life.
2) High-level flame retardant performance
In recent years, with the rapid development of the electronic and electrical industry and the continuous innovation of precision injection molding technology, thin-walled and refined plastic parts have become a development trend. Thin-walled flame-retardant products mean more sophisticated parts, which can make the product size smaller., Material usage and efficiency are higher, but thin-walled also brings new problems, that is, the decline of flame-retardant grade. In order to make up for the decline of flame-retardant grade caused by thin-wall, the addition of flame retardant components tends to lead to a decrease in mechanical properties.
This ultra-tough flame retardant PBT innovative material can well balance the mechanical properties and high flame retardant grade. While ensuring that the material reaches the ultra-tough grade, the flame retardant grade can also reach UL 94 V-0 (0.8mm), which can meet the use requirements of electronic connectors.

Several common electronic products need to achieve flame retardant grade
3) Good liquidity:
The high fluidity of plastics means that more complex and thin-walled products can be designed, injection molding can be easier and work efficiency can be improved. The addition of toughening agents will inevitably cause the fluidity of materials to decrease. This innovative material adopts high flow modification technology, which can greatly improve the fluidity of materials while ensuring super toughness level, and can reach the fluidity level of ordinary non-toughened PBT materials.
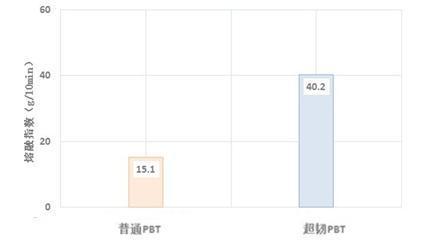
Comparison of melt finger between super-tough modified PBT and ordinary modified PBT (250 ℃ * 5kg)
4) Excellent electrical properties:
Arc resistance characterizes the ability of a material to resist deterioration caused by high-voltage arc action, usually expressed in seconds by the time required for the standard arc flame to cause charring on the surface of the material to conduct electricity on the surface and the arc to disappear. The following figure shows the arc resistance of PBT and several other engineering plastics. The figure shows that the arc resistance time of PBT engineering plastics is significantly higher than that of PC materials, which is the same as nylon and has good electrical properties.
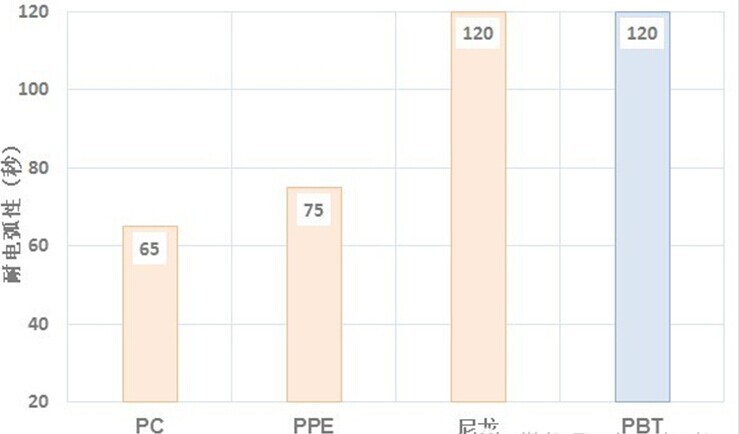
Comparison of arc resistance between PBT and common engineering plastics
In summary, this ultra-tough flame retardant PBT innovative material can achieve a comprehensive balance of processing fluidity, high-grade flame retardant, electrical properties, mechanical properties, etc., and is an ideal material that can be applied to the field of electronic connectors.







