
Fire prevention and smoke prevention ----- the "low smoke" performance of flame retardant products has attracted more and more attention

Fires bring heavy casualties and property losses to people every year. According to statistics from the Fire Department of the Ministry of Public Security, a total of 125402 fires were reported nationwide in 2011, with 1106 deaths and 572 injuries, and direct property losses exceeding 1.88 billion yuan.
Fire statistics show that 60-80% of the deaths in the fire are related to the smoke in the fire. The combustion products have three forms: gaseous, liquid and solid. The liquid and solid products are suspended in the air to form smoke and dust. When the smoke containing a large amount of smoke and dust is inhaled by the personnel in the fire scene, it will adhere to the nasal cavity, oral cavity and airway, and even enter the lungs and adhere to the alveoli by diffusion, in severe cases, it will block the nasal cavity and trachea, and eventually suffocate to death. In addition, the fire smoke has a strong shielding use of visible light, which greatly reduces the visibility. The hydrogen chloride, ammonia and chlorine in the fire smoke have a strong stimulation to the eyes, which makes people unable to open their eyes and seriously affects the speed of escaping from the scene. The large amount of smoke generated at the fire scene will make people feel horrible, panic, lose their minds, and cause chaos to the fire escape, which is very harmful. Therefore, "smoke" has become one of the most harmful killers in fire.
Plastics produce combustion gases and fire residues-like natural substances-that are always a potential toxic hazard. In many cases, injury to persons after inhalation of combustion gases can be prevented by taking certain measures. These measures specifically include limiting flammability and flame spread, establishing escape routes, establishing smoke and heat exhaust systems, and fire detection and firefighting. Where there is limited or no possibility of escape (e. g. in a train passing through a tunnel, on an aircraft, on a ship, etc.), the composition of combustion gases is generally considered a safety-relevant factor. The toxicity of combustion gases depends not only on the materials involved. The description of the fire scene (e. g. temperature, amount of oxygen) has an important influence on this.
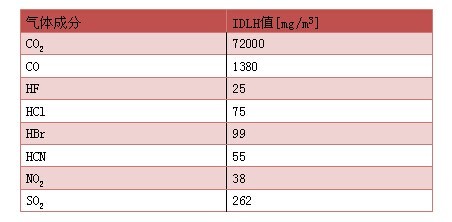
Combustion can produce a large number of various substances as by-products and can have potentially lethal effects. A comparison of the concentrations of the relevant components in the combustion gases with known limit concentrations allows an assessment of potential toxic hazards. IDLH (immediate danger to life and health) values are usually used as a basis. It is usually assumed that if the IDLH value is not exceeded, it is possible to escape within 30 minutes. In order to make predictions, Haber's rule is generally used: "If the product is exposed to the same concentration and exposure time, the effect will be the same." Therefore, for each gas component, the definition of its effective exposure dose refers to the product of its IDLH value (concentration) and the basal time (30 minutes).
For materials, in order to minimize the harm caused by fire, we must first improve the flame retardancy of the products and reduce the possibility of fire. However, although the polymer flame retardant modification can effectively suppress the "fire", it cannot completely eliminate the fire hazard. The flame retardant polymer can still burn violently in the fire. Therefore, the characteristics of flame retardant materials when burning should be paid more attention, and the composition of the combustion gas is usually regarded as a safety-related factor.
It is generally believed that when halogen flame retardant system burns, it will produce a large amount of smoke and toxic and corrosive hydrogen halide gas, causing secondary hazards. In the formulation design, consideration should be given to the development of efficient flame retardant system. In terms of flame retardant selection, low halogen halogen-free flame retardant system should be adopted to reduce the amount of halogen flame retardant, or smoke suppression agent should be added to reduce the generation of smoke. At present, engineers and technicians are increasingly focusing on the development of halogen-free, low-smoke, low-toxicity and high-efficiency flame-retardant materials. There are numerous companies and universities engaged in the research of low-smoke halogen-free (LSOH) flame-retardant technology for polymers in the world, among which large chemical companies include Shell, DuPont, BASF, Bayer, Exxon, GE Chemical, Heast Chemical, Toyota, etc, the overall domestic research level is basically synchronized with the international advanced level. We look forward to the introduction and use of more low-smoke, low-toxicity flame-retardant products to truly "protect the environment and protect people".







